The rise of coronavirus variants has highlighted the huge influence evolutionary biology has on daily life. But how mutations, random chance and natural selection produce variants is a complicated process, and there has been a lot of confusion about how and why new variants emerge.
Until recently, the most famous example of rapid evolution was the story of the peppered moth. In the mid-1800s, factories in Manchester, England, began covering the moth’s habitat in soot, and the moth’s normal white coloring made them visible to predators. But some moths had a mutation that made them darker. Since they were better camouflaged in their new world, they could evade predators and reproduce more than their white counterparts.
We are an evolutionary biologist and an infectious disease epidemiologist at the University of Pittsburgh who work together to track and control the evolution of pathogens. Over the past year and half, we’ve been closely following how the coronavirus has acquired different mutations around the world.
It’s natural to wonder if highly effective COVID-19 vaccines are leading to the emergence of variants that evade the vaccine – like dark peppered moths evaded birds that hunted them. But with just under 40% of people in the world having received a dose of a vaccine – only 2% in low-income countries – and nearly a million new infections occurring globally every day, the emergence of new, more contagious variants, like delta, is being driven by uncontrolled transmission, not vaccines.
How a virus mutates
For any organism, including a virus, copying its genetic code is the essence of reproduction – but this process is often imperfect. Coronaviruses use RNA for their genetic information, and copying RNA is more error-prone than using DNA. Researchers have shown that when the coronavirus replicates, around 3% of new virus copies have a new, random error, otherwise known as a mutation.
Each infection produces millions of viruses within a person’s body, leading to many mutated coronaviruses. However, the number of mutated viruses is dwarfed by the much larger number of viruses that are the same as the strain that started the infection.
Nearly all of the mutations that occur are harmless glitches that don’t change how the virus works – and others in fact harm the virus. Some small fraction of changes may make the virus more infectious, but these mutants must also be lucky. To give rise to a new variant, it must successfully jump to a new person and replicate many copies.
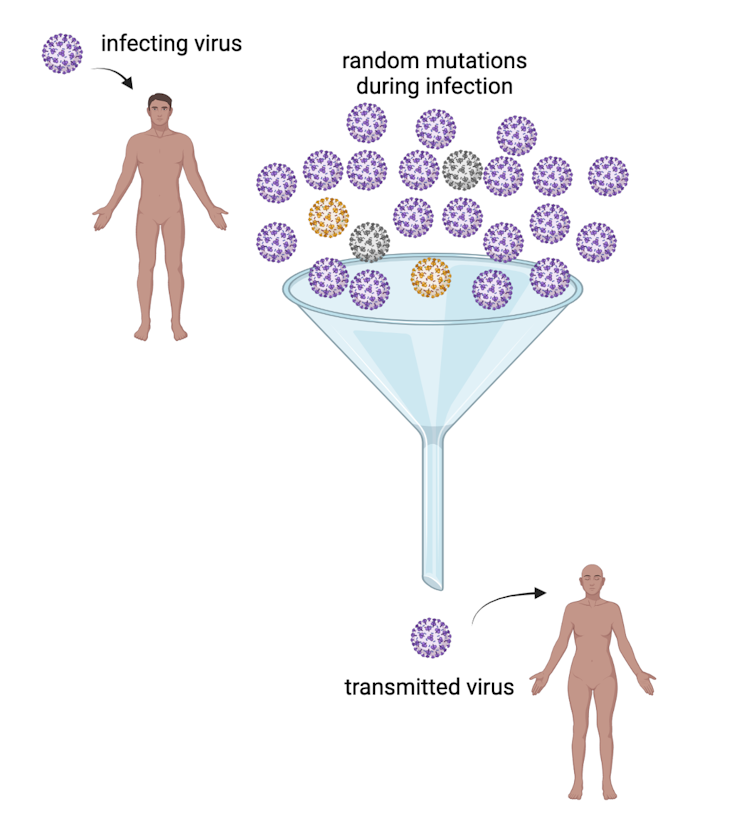
Transmission is the important bottleneck
Most viruses in an infected person are genetically identical to the strain that started the infection. It is much more likely that one of these copies – not a rare mutation – gets passed on to someone else. Research has shown that almost no mutated viruses are transmitted from their original host to another person.
And even if a new mutant causes an infection, the mutant viruses are usually outnumbered by non-mutant viruses in the new host and aren’t usually transmitted to the next person.
The small odds of a mutant being transmitted is called the “population bottleneck.” The fact that it is only a small number of the viruses that start the next infection is the critical, random factor that limits the probability that new variants will arise. The birth of every new variant is a chance event involving a copying error and an unlikely transmission event. Out of the millions of coronavirus copies in an infected person, the odds are remote that a fitter mutant is among the few that spread to another person and become amplified into a new variant.
How do new variants emerge?
Unfortunately, uncontrolled spread of a virus can overcome even the tightest bottlenecks. While most mutations have no effect on the virus, some can and have increased how contagious the coronavirus is. If a fast-spreading strain is able to cause a large number of COVID-19 cases somewhere, it will start to out-compete less contagious strains and generate a new variant – just like the delta variant did.
Many researchers are studying which mutations lead to more transmissible versions of the coronavirus. It turns out that variants have tended to have many of the same mutations that increase the amount of virus an infected person produces. With more than a million new infections occurring every day and billions of people still unvaccinated, susceptible hosts are rarely in short supply. So, natural selection will favor mutations that can exploit all these unvaccinated people and make the coronavirus more transmissible.
Under these circumstances, the best way to constrain the evolution of the coronavirus is to reduce the number of infections.
Vaccines stop new variants
The delta variant has spread around the globe, and the next variants are already on the rise. If the goal is to limit infections, vaccines are the answer.
Even though vaccinated people can still get infected with the delta variant, they tend to experience shorter, milder infections than unvaccinated individuals. This greatly reduces the chances of any mutated virus – either one that makes the virus more transmissible or one that could allow it to get past immunity from vaccines – from jumping from one person to another.
Eventually, when nearly everyone has some immunity to the coronavirus from vaccination, viruses that break through this immunity could gain a competitive advantage over other strains. It is theoretically possible that in this situation, natural selection will lead to variants that can infect and cause serious disease in vaccinated people. However, these mutants must still escape the population bottleneck.
For now, it is unlikely that vaccine-induced immunity will be the major player in variant emergence because there are lots of new infections occurring. It’s simply a numbers game. The modest benefit the virus would get from vaccine evasion is dwarfed by the vast opportunities to infect unvaccinated people.
The world has already witnessed the relationship between the number of infections and the rise of mutants. The coronavirus remained essentially unchanged for months until the pandemic got out of control. With relatively few infections, the genetic code had limited opportunities to mutate. But as infection clusters exploded, the virus rolled the dice millions of times and some mutations produced fitter mutants.
The best way to stop new variants is to stop their spread, and the answer to that is vaccination.
ABOUT THE AUTHORS
Vaughn Cooper is an evolutionary biologist and microbiologist who studies the evolution of infectious disease and how microbes and cancers adapt to new environments and hosts. He is currently Professor of Microbiology and Molecular Genetics, and Computational and Systems Biology, at the University of Pittsburgh, School of Medicine. He co-founded and is Director of the Center for Evolutionary Biology and Medicine. He received his bachelor’s degree from Amherst College and his Ph.D. in 2000 from Michigan State University under the mentorship of Richard Lenski, where he studied the evolution of specialization in the Long-Term Evolution Experiment of E. coli populations. He was a Postdoctoral Fellow of the Michigan Society of Fellows at the University of Michigan, studying pathogens of the cystic fibrosis airway with John LiPuma. He was Assistant and Associate Professor at the University of New Hampshire from 2004-2015, moving to the University of Pittsburgh in 2015. . His awards include the 2010 Outstanding Assistant Professor at UNH and an NSF CAREER award. After serving as Chair of the Council of Microbial Sciences for the American Society of Microbiology, he was elected to the Board of Directors. His research is supported by the NIH, NSF, NASA, and by the Cystic Fibrosis Foundation. The Cooper laboratory studies how bacterial populations (e.g. Burkholderia, Pseudomonas, Acinetobacter, and multispecies communities) evolve to adapt to new hosts and environments, particularly in biofilms. Other major interests include the evolution of SARS-CoV-2, the evolution of antimicrobial resistance and why genome regions mutate/evolve at different rates. We also develop and promote a laboratory curriculum called EvolvingSTEM that enables high school students to learn the practice of life science research and key topics in evolution and heredity by conducting a weeklong experiment with bacteria.
Lee Harrison, Professor of Epidemiology, Medicine, and Infectious Diseases and Microbiology, University of Pittsburgh. Dr. Harrison is an infectious diseases physician whose research focuses on the epidemiology and genomic epidemiology of serious infectious pathogens, including S. pneumoniae, N. meningitidis, C. difficile, influenza and SAR-CoV-2. A current project involves novel genomic and computational methods for early detection of outbreaks of bacterial and viral pathogens in the hospital. This approach uses whole genome sequencing surveillance and data mining of the electronic health record using machine learning to identify serious outbreaks that are missed by traditional hospital epidemiologic methods.
This article is courtesy of The Conversation.