New research findings point toward a class of compounds that could be effective in combating infections caused by enterovirus D68, which has stricken children with serious respiratory infections and might be associated with polio-like symptoms in the United States and elsewhere.
The researchers have used a technique called X-ray crystallography to learn the precise structure of the original strain of EV-D68 on its own and when bound to an anti-viral compound called “pleconaril.”
The ongoing research could lead to the development of drugs that inhibit infections caused by the most recent strains of the virus, said Michael G. Rossmann, Hanley Distinguished Professor of Biological Sciences at Purdue University.
The Pocket Factor
A molecule called a “pocket factor” is located within a pocket of the virus’s protective shell, called the capsid. When the virus binds to a human cell, the pocket factor is squeezed out of its pocket resulting in the destabilization of the virus particle, which then disintegrates and releases its genetic material to infect the cell and to replicate itself.
The antiviral compound pleconaril also binds into the pocket, inhibiting infection.
“The compound and the normal pocket factor compete with each other for binding into the pocket,” Rossmann said. “They are both hydrophobic, and they both like to get away from water by going into the pocket. But which of these is going to win depends on the pocket itself, the pocket factor and properties of the antiviral compound.”
“In this work we only focused on the very original EV-D68 isolate, which was discovered in 1962,” Liu said. “Strains in the current outbreaks have minor differences.”
Although pleconaril is not active against current strains of EV-D68 tested thus far, it is active against the original isolate. Small changes in the structure of pleconaril are likely to lead to anti EV-D68 inhibitors against a broader spectrum of isolates.
An upsurge of EV-D68 cases in the past few years has shown clusters of infections worldwide. In August 2014 an outbreak of mild-to-severe respiratory illnesses occurred among thousands of children in the United States of which 1,149 cases have been confirmed to be caused by EV-D68. The virus also has been associated with occasional neurological infections and “acute flaccid myelitis,” characterized by symptoms including muscle weakness and paralysis. Although EV-D68 has emerged as a considerable global public health threat, there is no available vaccine or effective antiviral treatment.
Research led by Rossmann, working with pharmaceutical companies, has resulted in antiviral drugs for other enteroviruses such as rhinoviruses that cause common cold symptoms. These drugs include pleconaril, which was developed in the 1990s but not approved by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration primarily because of a side effect that puts women using birth control drugs at risk of conception.
EV-D68 and Acute Flaccid Paralysis
Purdue researchers became interested in studying pleconaril’s potential effectiveness against EV-D68 after an outbreak of about 20 cases of acute flaccid paralysis was reported in California between 2012 and 2014. Out of those cases, two tested positive for EV-D68.
“This suggests the potential association of EV-D68 with polio-like illness,” said Yue Liu, a graduate student working on the project.
The researchers are working with the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention and are studying these newer strains to determine their structures.
“The need for an effective antiviral agent for treatment of EV-D68 infections was made apparent by the widespread and large numbers of EV-D68 infections (in 2014), many of which were associated with significant morbidity,” said Mark A. McKinlay, director of the Center for Vaccine Equity at the Task Force for Global Health.
“The determination of the structure of the EV-D68 reported here by Michael Rossmann and his team represents an important step in this direction. The strain of EV-D68 used in the study is from 1962, and Michael’s team along with Steve Oberste’s group at CDC have shown that this strain is inhibited by pleconaril at clinically achievable concentrations. Testing of pleconaril against the current circulating strains at CDC thus far showed these strains are not susceptible to the antiviral compound,” said McKinlay, who who collaborates with the CDC on polio eradication efforts, and has been a key figure in pharmaceutical-company collaborations with Rossmann’s group to discover and develop pleconaril.
Once the newer strains are better understood, the ongoing research could yield compounds that are effective against these strains.
“Designing the best possible compound for these newer strains will take more time, but I hope that in a year or so we might have something,” Rossmann said.
Like EV-D68 and EV71, poliovirus is an enterovirus and is within the large family called picornaviruses. Non-polio enteroviruses are common viruses and cause about 10 to 15 million infections in the United States each year, but most infected individuals have only mild illness, similar to a common cold, according to the CDC.
The findings are detailed in a paper appearing in the journal Science: Structure and inhibition of EV-D68, a virus that causes respiratory illness in children.
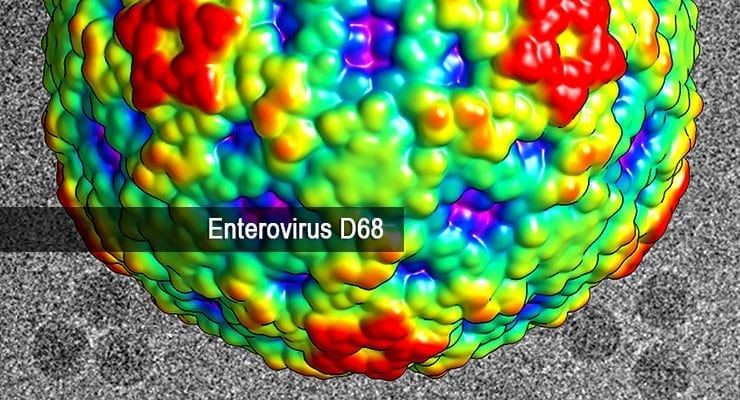
Image: This color-coded image shows the surface view of enterovirus D68, which has stricken children with serious respiratory infections and might be associated with polio-like symptoms. Red regions are the highest peaks, and the lowest portions are blue. In the black-and-white background are actual electron microscopy images of the EV-D68 virus. Credit: Yue Liu and Michael G. Rossmann/Purdue University.
Editor’s Note: The Center for Infectious Disease Research and Policy (CIDRAP) did an excellent job covering the EVD68 outbreak in 2014. Access their articles here.