The Defense Advanced Research Projects Agency (DARPA) this month awarded a new contract under a program aiming to develop co-evolving therapy platforms to protect defense personnel and the public against rapidly evolving viral pathogens and biothreats.
The Defence Science and Technology Laboratory (Dstl) at Porton Down will support the INTERfering and Co-Evolving Prevention and Therapy (INTERCEPT) program under a contract valued at $997,726 plus options totaling $448,317.
Current preventive and therapeutic approaches, including vaccines and anti-viral drugs, are designed to target the virus in its original state at the time of discovery or diagnosis. This paradigm of “static” therapeutics and preventives requires repeated and time-consuming development, manufacturing, and testing, resulting in major health response gaps, economic burden, and limited capability to address newly emerging biothreats.
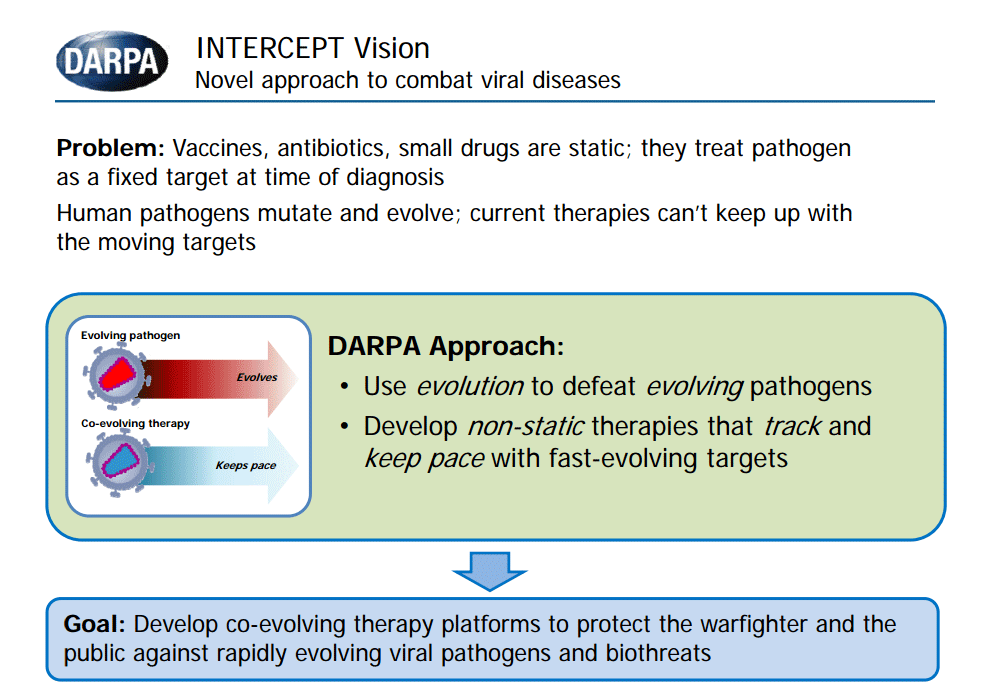
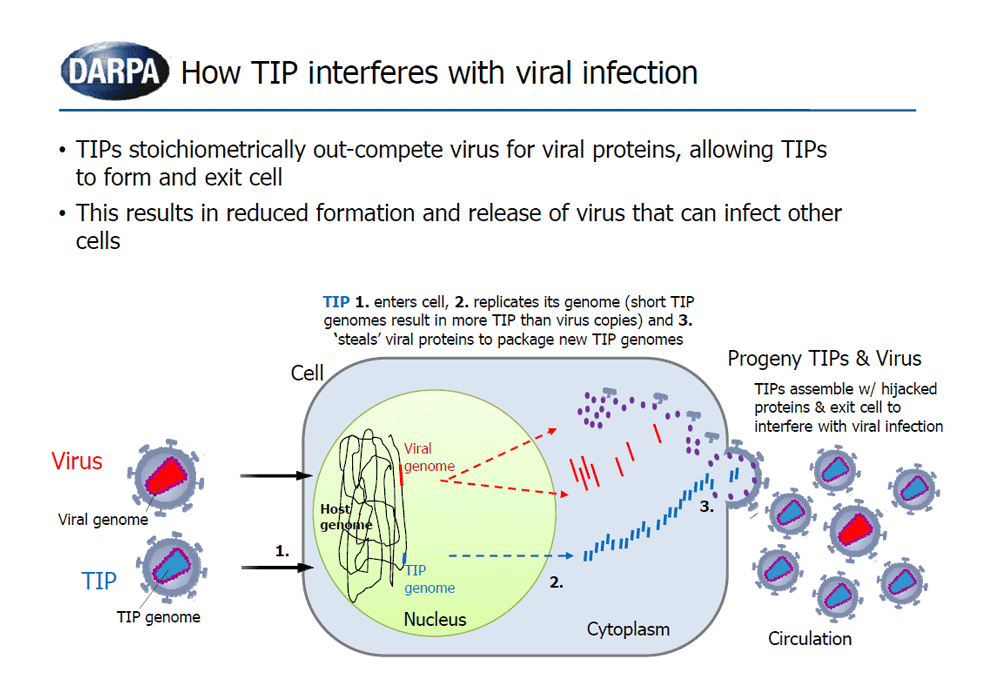
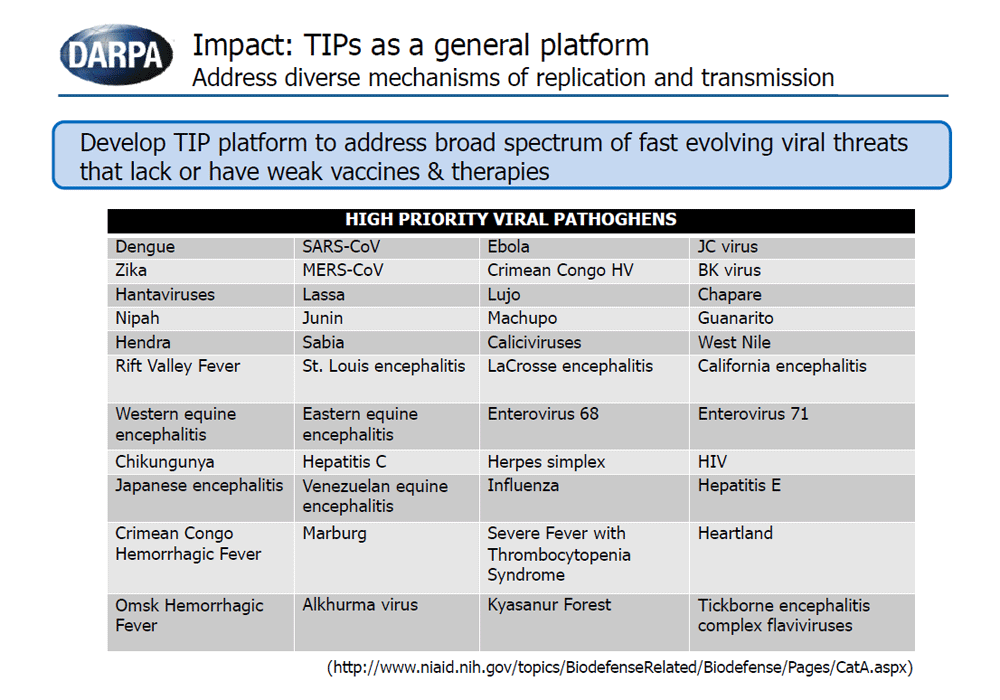
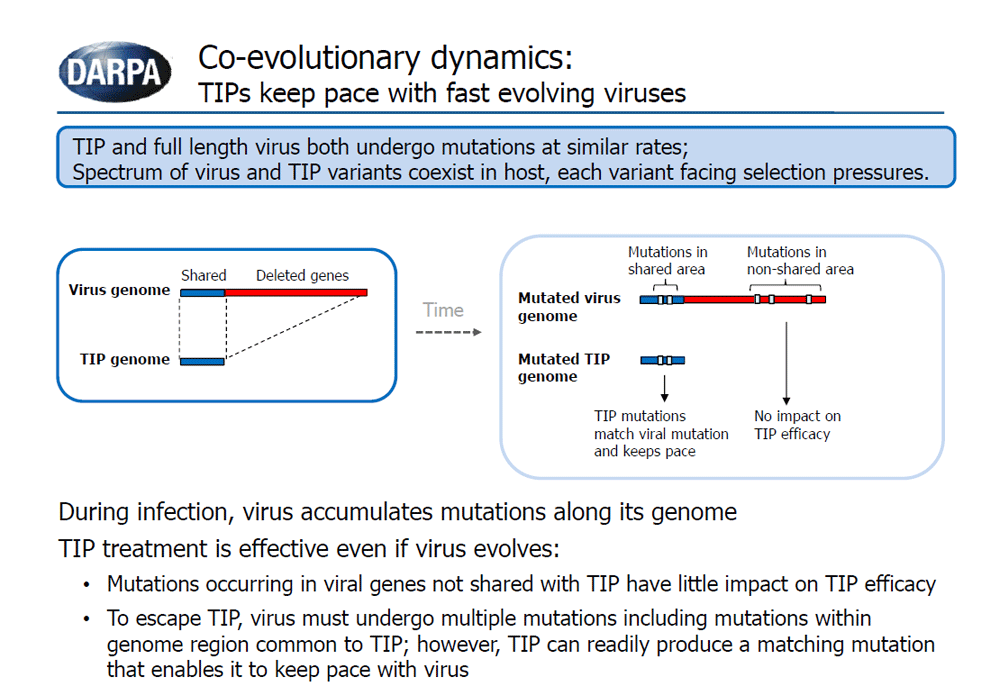
The goal of the INTERCEPT program is to develop and explore the potential use of Therapeutic Interfering Particles, or TIPs, as a dynamic approach to address rapidly evolving viral pathogens. TIPs are virus-derived particles with defective genomes that can only replicate in the presence of the virus, interfering with viral infection through competition for essential viral components. Just like their parent virus, TIPs are susceptible to mutation over time and can co-evolve with the mutating virus, mitigating virus evasion from the therapeutic.
The novel path explored in this program is based upon previously reported Defective Interfering Particles (DIPs), viral-derived particles with partially deleted genomes that arise during a natural infection. DIPs lack genes encoding replication enzymes and capsid proteins, and thus require co-infection with the wildtype parent virus to replicate and mobilize. DIPs have been isolated from numerous viral infections and shown to interfere with the replication and packaging processes through stoichiometric competition for essential viral components.
 To explore the TIP concept as a potential therapeutic and/or preventive platform that can keep pace with fast-evolving pathogens, INTERCEPT will address four fundamental questions:
To explore the TIP concept as a potential therapeutic and/or preventive platform that can keep pace with fast-evolving pathogens, INTERCEPT will address four fundamental questions:
- Safety & efficacy: Can TIPs be built that are safe and out-compete the pathogen to control infections short-term?
- Co-evolution: Can TIPs evolve and keep pace with evolving pathogens to control an infection long-term?
- Population-scale efficacy: Can TIPs co-transmit alongside pathogen to help control the spread of infectious disease across populations?
- Generalizability: Can the TIP concept be extended across multiple viruses and for multiple acute and chronic infectious diseases?
The INTERCEPT program is expected to encompass a four-year effort organized in two phases of two years duration each. During the Phase I period, performer teams such as Dstl will establish proof-of-concept of TIPs safety, broad range efficacy, and initial TIP-pathogen coevolution using in vitro and in vivo models of viral infection, as well as mathematical models of TIP-pathogen-host dynamics. The Phase II period will focus on the validation of long-term TIP safety and efficacy, long-term co-evolution studies, and TIP co-transmission dynamics for population-scale disease control.
Sources: DARPA, FBO.gov