The National Institute of Allergy and Infectious Diseases’ Rocky Mountain Laboratories (RML) has produced images of the novel coronavirus (SARS-CoV-2, previously known as 2019-nCoV), the causative pathogen of Coronavirus Disease (COVID-19), on its scanning and transmission electron microscopes this week.
Note that the images do not look much different from MERS-CoV (Middle East respiratory syndrome coronavirus, which emerged in 2012) or the original SARS-CoV (severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus, which emerged in 2002). That is not surprising: The spikes on the surface of coronaviruses give this virus family its name – corona, which is Latin for “crown,” and most any coronavirus will have a crown-like appearance.
RML investigator Emmie de Wit, Ph.D., provided the virus samples as part of her studies. Microscopist Elizabeth Fischer produced the images, and the RML visual medical arts office digitally colorized the images.
The images are available free to the public on the NIAID Flickr page. NIAID asks all who use the images to please credit NIAID-RML.
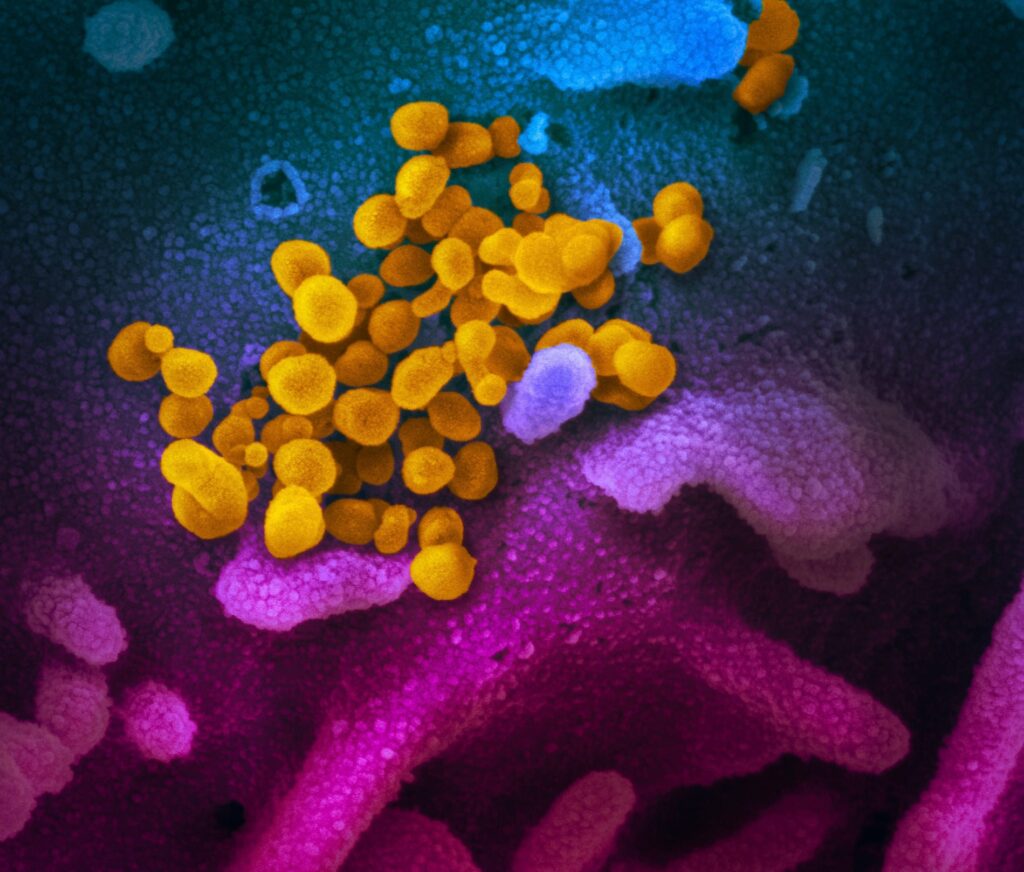
This scanning electron microscope image shows SARS-CoV-2 (yellow)—also known as 2019-nCoV, the virus that causes COVID-19—isolated from a patient in the U.S., emerging from the surface of cells (blue/pink) cultured in the lab. Credit: NIAID-RML
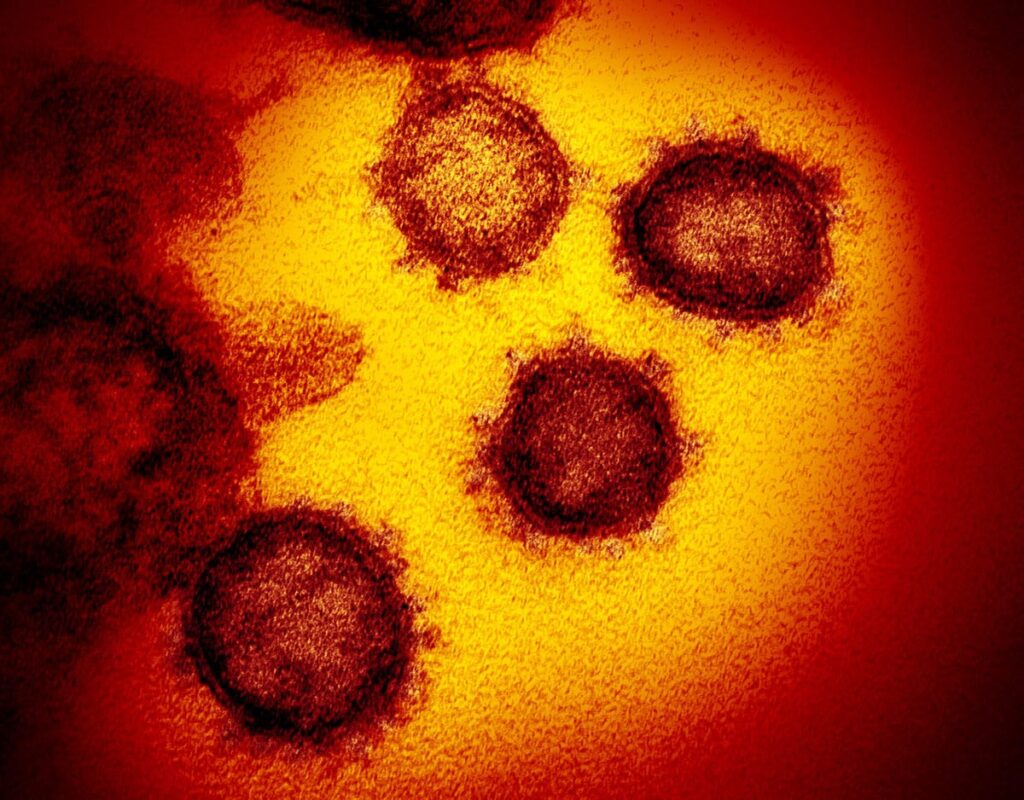
This transmission electron microscope image shows SARS-CoV-2—also known as 2019-nCoV, the virus that causes COVID-19. isolated from a patient in the U.S., emerging from the surface of cells cultured in the lab. Credit: NIAID-RML
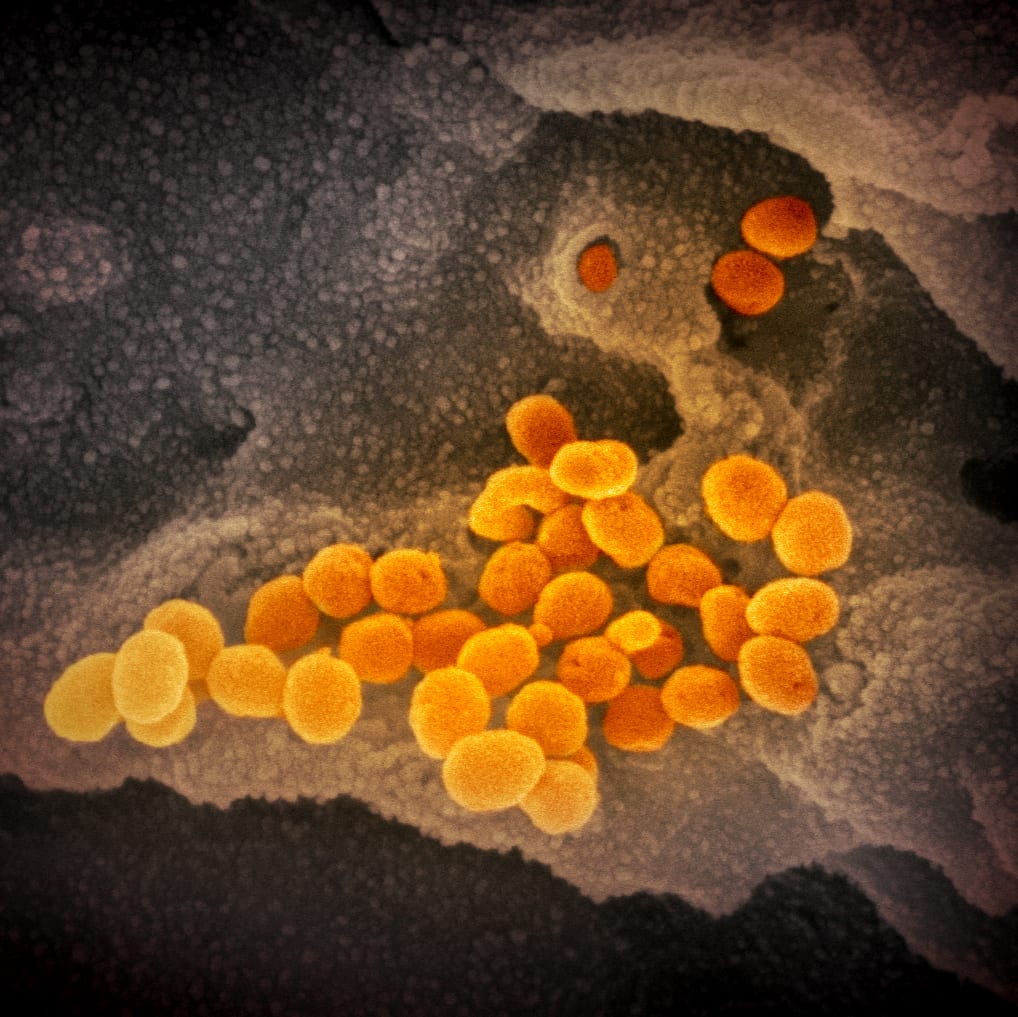
This scanning electron microscope image shows SARS-CoV-2 (orange)—also known as 2019-nCoV, the virus that causes COVID-19—isolated from a patient in the U.S., emerging from the surface of cells (gray) cultured in the lab. Credit: NIAID-RML
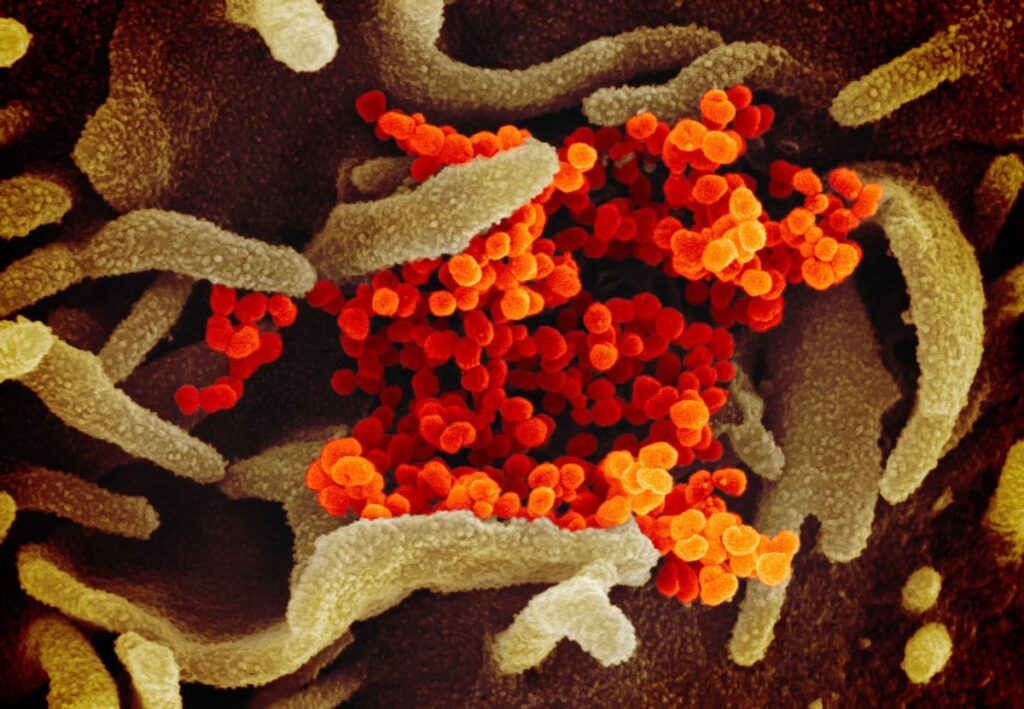
This scanning electron microscope image shows SARS-CoV-2 (orange)—also known as 2019-nCoV, the virus that causes COVID-19—isolated from a patient in the U.S., emerging from the surface of cells (green) cultured in the lab. Credit: NIAID-RML


