 The World Health Organization (WHO) yesterday announced nine additional laboratory-confirmed cases of influenza A(H7N9) in China, bringing the official total to 64 infections, 14 of which have died.
The World Health Organization (WHO) yesterday announced nine additional laboratory-confirmed cases of influenza A(H7N9) in China, bringing the official total to 64 infections, 14 of which have died.
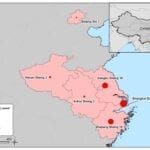
Of the latest laboratory confirmed cases, four are from Zhejiang, three are from Shanghai and two from Jiangsu. Previously, the virus had only been reported in Shanghai and neighboring regions.
So far there is no evidence, based on monitoring of more than 1,000 close contacts, of sustained human-to-human transmission, says the WHO. The spreading into new geographical territories could however represent limited person-to-person transmission.
“I think we need to be very, very concerned” about these developments, says Jeremy Farrar, Director of the Oxford University Clinical Research Unit in Ho Chi Minh City, Vietnam. (Source: Nature)
Investigations into the possible sources of infection and reservoirs of the virus are ongoing.
About H7N9
Influenza A(H7) viruses are a group of influenza viruses that normally circulate among birds. The influenza A(H7N9) virus seen in China is a reassortant virus containing genes from A(H7N9) and A(H9N2). It is genetically distinct from other A(H7N9) viruses previously identified in wild bird and poultry populations. This virus does not appear to cause severe illness in avian populations, and represents the first H7N9 subtype to cause infection in humans.
Image credit: European Centre for Disease Prevention and Control


