The Nutritional Immunology and Molecular Medicine Laboratory (NIMML), with research funding assistance from the Defense Threat Reduction Agency (DTRA), has developed a high-resolution model of the gut immune system to help solve emerging and re-emerging infectious diseases and biodefense challenges.
The advanced model predicts new emerging behaviors and responses to biological threats. The gut ecosystem includes trillions of interactions between host epithelial and immune cells, molecules (cytokines, chemokines and metabolites) and microbes is a massively and dynamically interacting network, like a multidimensional jigsaw puzzle with pieces that are constantly changing shape. These interactions with cooperativity and feedback lead to nonlinear dynamics and unforeseen emergent behaviors across spatiotemporal scales.
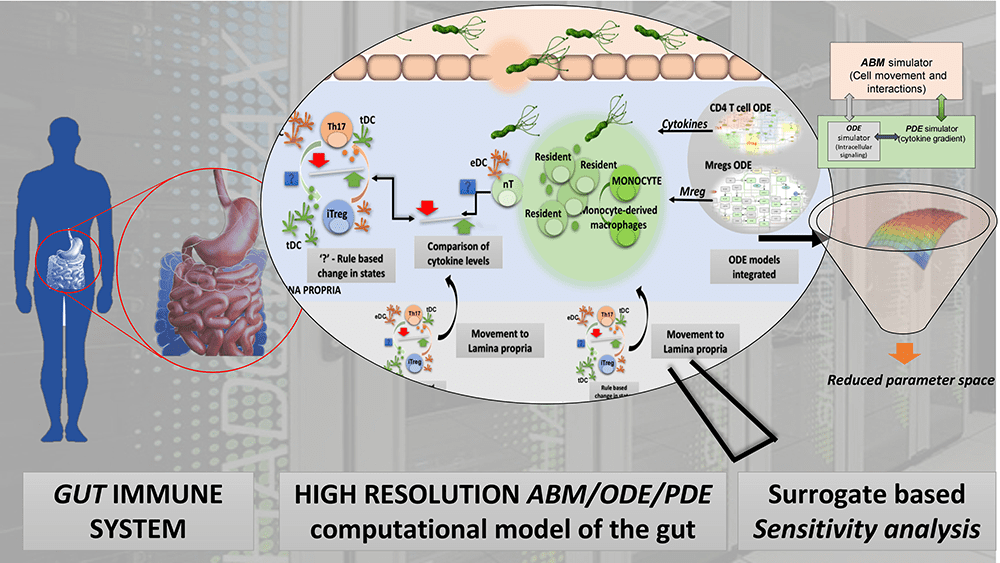
The NIMML agent-based modeling (ABM) of the gut uses an array of HPC-driven advanced computational technologies such as the ENteric Immunity SImulator (ENISI) – multiscale modeling (MSM). These models and tools simulate cell phenotype changes, signaling pathways, immune responses, lesion formation, cytokine, chemokine and metabolite diffusions, and cell movements at the gut mucosa.
ENISI MSM is a cutting-edge tool at the forefront of advanced computational modeling and simulation of biological systems. ENISI fully integrates agent-based modeling (ABM) with other computational and mathematical modeling technologies including differential equations-based methods such as ODE and PDE.
NIMML recently published a study in Gigascience where the HPC-driven ENISI MSM multiscale model was used to investigate the underlying immunological mechanisms that promote host tolerance to Helicobacter pylori infection in the gut. H. pylori colonizes the stomach, one of the harshest environments a microbe encounters, of 50% of the human population and persists for prolonged periods of time, often causing a lifelong infection. Although H. pylori causes gastric cancer in 1-2% of cases, it exerts beneficial health effects including protection against allergies and gastroesophageal diseases. The majority of H. pylori colonized individuals, an estimated 85%, do not present any detrimental effects.
“We are pleased to present the first high-resolution, multiscale model of the stomach during infection with H. pylori. This model culminates many years of work at the interface of modeling and immunology experimentation by combining the use of ODE to model intracellular signaling pathways, in combination with PDEs to simulate cytokine, chemokine diffusions and ABM for modeling cell-cell interactions at the cellular and population levels,” said Dr. Hontecillas, the co-Director of NIMML. “The model has been developed, analyzed and calibrated against experimental data with the aim of determining the mechanistic interactions responsible for observed immune profiles.”
“NIMML’s advanced HPC-driven computational modeling capabilities and artificial intelligence (AI) algorithms in combination with innovative experimental methods have major applications in transforming biodefense. These models are being used in a DTRA-funded project to evaluate several scenarios of possible therapeutic interventions during biological or chemical threats,” said Dr. Josep Bassaganya-Riera, the Director of NIMML. “As a part of a productive NIMML-led collaboration with the Department of Industrial and Systems Engineering at Virginia Tech and Geisinger Healthcare System, we will continue to apply these advanced computational modeling methods for gaining new valuable insights on the mechanisms that delineate functional fates of immune cells and influence disease outcomes during infection.”
Sensitivity analysis methods for the ABMs are still immature. Researchers at NIMML used the outputs for global multi-resolution sensitivity analysis (SA). Building a surrogate model reduced the computational time to run simulations. These new SA methods identified epithelial cells, macrophages and dendritic cells as key factors that delineate the outcome of the infection.
“NIMML’s advanced machine learning based approaches for SA replaced the computational and time-expensive ABM with a surrogate model reducing the computational costs, thereby enabling greater scalability. We used this AI approach to analyze the influential parameters underlying the H. pylori infection,” said Meghna Verma, a NIMML PhD student. “We performed, in silico validation with the results we obtained using our metamodel and discovered that the colonization of H. pylori decreased with a decrease in epithelial cell proliferation and this decrease was mediated by regulatory macrophages and tolerogenic dendritic cells.”
Source: Nutritional Immunology & Molecular Medicine. Edited by Stephanie Lizotte



